A fracture of the femoral neck is a serious injury, especially for the elderly. There is trauma to the thinnest part of the thigh – the neck, which connects the body of the bone with its head. Fractures are especially common with the onset of ice in the cold season. Let’s look at what provoking factors increase the incidence of injuries and what are the alternatives to treatment.
WHAT ARE THE TYPES OF FRACTURES?
Depending on the anatomical location of the fracture, there are:
Subcapital: the fracture line passes just below the head of the femur.
Transcervical: the fracture line crosses the central part of the femoral neck.
Basiscervical: the fracture line is localized at the bottom of the femoral neck.
There is also a separate classification of Garden and Powells. The first classification is based on the degree of fracture:
And type: incomplete fracture, the apex of the bone is slightly rotated around the axis;
Type II: complete fracture without displacement, the fragments are held in their natural position only by the ligament;
Type III: complete fracture with partial displacement;
Type IV: complete fracture with violation of the integrity of the ligament, the fragments are separated and completely displaced. Powell’s classification is based on an estimate of the angle between the axis of the femur and the fracture line.
WHO IS AT RISK?
Fracture is considered the most dangerous for the elderly, because the recovery period is very difficult and in most cases the person remains disabled. Women at menopause also have an increased risk of developing a fracture, as hormonal changes occur with age, which lead to the fragility of bone tissue.
MANIFESTATIONS OF PATHOLOGY
The appearance of pain in the groin, especially when moving the foot and on palpation.
The affected limb becomes a few centimeters shorter than the healthy one, the patient cannot even lift it lying on his back (“stuck heel” syndrome).
Occurrence of a hematoma in the groin area: occurs a few days after the fracture, but in the presence of excess body weight, the hematoma may be invisible.
The foot is turned outwards relative to the knee.
DIAGNOSIS
Examination methods will include physical examination, palpation, and medical history. Additionally, radiography is performed to confirm the diagnosis and determine the type of fracture.
TREATMENT
Of great importance is the provision of first aid in the development of fractures of the femoral neck, otherwise the high risk of disability or death. So first aid will be to call an ambulance, the victim must be placed on a hard surface. In any case, you can not exercise the leg – it is important to ensure its complete immobilization, by applying the tire.
At the same time, the splint should not be placed on an open wound surface (a soft layer of tissue is placed under the bottom) and made too tight, as this may lead to tissue death.
The next step will be to deliver the victim to the hospital with the next treatment.
Treatment methods will depend on the type of fracture, its location and age of the patient.
So often at a young age the best treatment option is to stay in bed and one of the main methods of conservative treatment:
skeletal traction;
repositioning of fragments: application of a fixing bandage and subsequent movement with crutches;
drug therapy: drugs to improve metabolic processes in bone and cartilage, vitamin therapy.
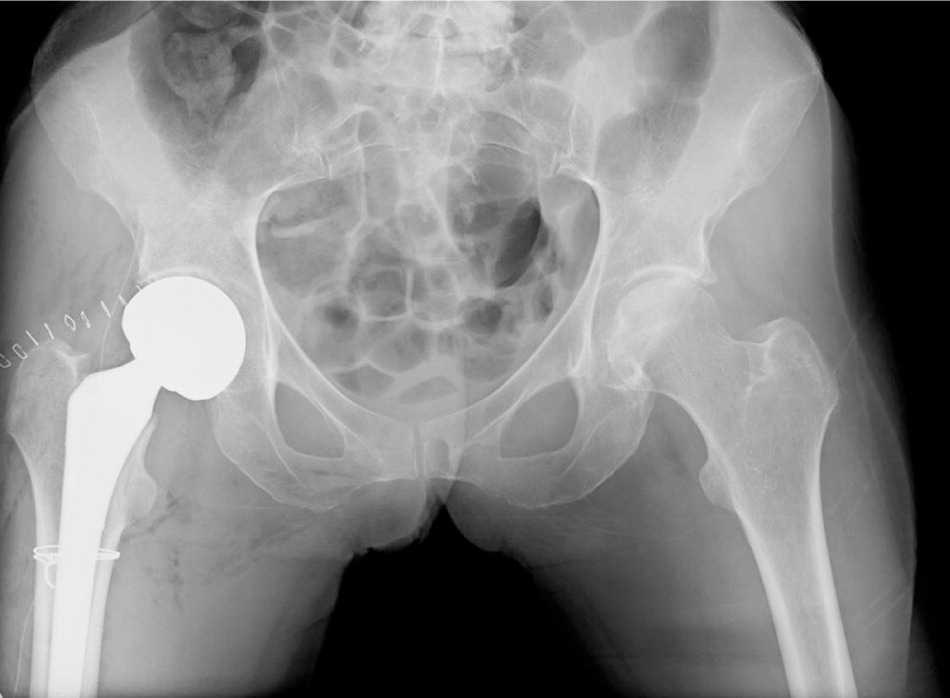
Surgery is performed with poor bone fusion, respectively, is fixed with screws or replacement of the affected head of the femoral neck with a prosthesis.
The resulting injury is quite complex and requires a long recovery and rehabilitation period, which must be under the supervision of specialists. So additional physiotherapy is massage, exercise therapy.
Remember that timely treatment, proper care and proper recovery will ensure the longevity of the patient with a fracture of the femoral neck.