Ukraine Gate- Kyiv – May 22, 2022 – The World Health Organization (WHO) has recorded about a hundred confirmed cases of monkeypox in 14 countries that are not endemic to the virus. Cases of monkeypox have been confirmed, in addition to those previously reported, in Israel and Switzerland.
As of Saturday, the World Health Organization (WHO) has recorded 92 confirmed cases and 28 probable cases of monkeypox.
According to the WHO, the largest number of cases was recorded in Britain, Spain and Portugal.
“The available information suggests that human-to-human transmission (of the virus) occurs among people who are in close physical contact with patients with symptoms,” the statement said.
It is noted that many of the current cases have been reported in sexual health clinics.
The WHO is expected to provide additional guidance and guidance to countries in the coming days on how to mitigate the effects of monkeypox.
monkeypox, which is usually found only in Africa, is now spreading in Europe and North America.
On May 7, the first case of the disease was recorded in the UK: the patient returned from Nigeria a few weeks ago. In two weeks, monkeypox cases were found in the United States, Canada, France, Italy, Spain, Portugal, Sweden and Australia.
The first case of human infection with monkeypox was recorded in 1970.
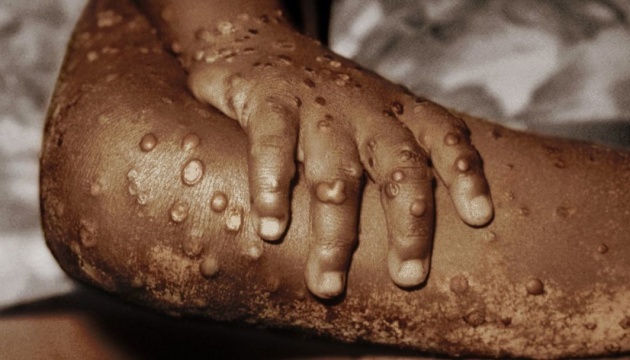
Infection usually occurs through close contact. The virus can enter the body through damaged skin, respiratory tract, tear of the eyes, nose or mouth. The disease is transmitted by contact with an infected animal (monkey, rat, squirrel), from an infected person to a person or through objects – clothing, bedding.
The incubation period lasts from 6 to 16 days. A person usually develops fever, headache, muscle pain, fatigue. Subsequently, there are characteristic rashes on the body. Most often the disease goes away on its own in two or three weeks. But in some cases the disease is severe. The mortality rate ranges from 1% to 15%. This disease is most difficult for children.