Kiev. Ukraine. Ukraine Gate – January 3, 2021 – Science
Researchers from several countries turned dangerous pesticides as a means of combating resistant bacteria. Its effectiveness is comparable to modern antibiotics.
N-Aryl-C-nitroazoles are an important class of heterocyclic compounds. They are used as pesticides and fungicides. However, these substances are toxic to humans and cause mutations. Researchers have repeatedly suggested that these groups of compounds may help in the fight against pathogenic bacteria. However, to reduce the toxic effects it is necessary to carry out a large amount of work at the molecular level.
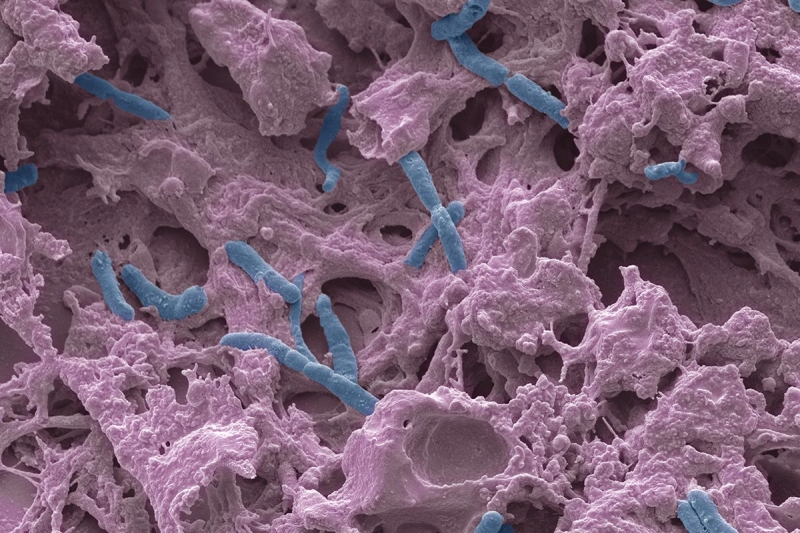
Now an international team of researchers has been able to establish that when treated, the compounds can fight against drug-sensitive strains of TB pathogens. At the same time, they were powerless against strains of pathogens belonging to the ESKAPE group (abbreviation of the names of bacterial species that most often develop resistance to antibiotics: Enterococcus faecium, Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomorogenes aerugin).
After that, the researchers again modified the compound and built two isomeric (identical in atomic location) series of substances. The side amino groups changed their position to make the aromatic nucleus of the nitrogen-rich substance more compact, which reduced the toxicity of the substance. The sensitivity of microorganisms to the new compound was tested by disco-diffusion method.
It turned out that the representatives of the ESKAPE group were easily suppressed by new substances. The minimum concentration of a chemical compound that prevents visible growth of bacteria or bacteria (μg / ml) for the test substance shows a result that can be compared with the action of the antibiotic ciprofloxacin. For example, enterococci require 0.3 μg / ml antibiotic or 2 μg / ml one of the new substances. At the same time M. Tuberculosis, whichpyrimidine OTB-021 was harmful at first, was completely insensitive to new substances.